The Top 10 Common Uses of Gold Today
Gold has been a valuable precious metal since ancient civilizations.
By Jane Pardo | Updated December 30, 2023
With its stunning lustrous appearance and outstanding metallic qualities, gold is considered useful in numerous industry sectors today. From accessories and electronics to dentistry and medicine, gold is ever present in our day-to-day life.
Keep reading to learn the most common uses of gold today. We will explore the ten most popular applications of this much-coveted, versatile metal in modern times.
Uses of Gold
1. Investment

While no longer a major type of currency, gold is an effective hedge against inflation and an excellent portfolio diversifier. Investors consider this much-sought-after precious metal a must-have in their long-term portfolios.
Historically, the price of gold increases when the cost of living rises and paper investments like stocks decline.
Investors consider gold a dependable store of value and a safe haven through turbulent economic and political times.
Investors generally do any of these steps to buy gold:
- Buy physical gold bullion for storage, such as gold bars and coins
- Invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds replicating the prices of gold by holding physical gold. These funds expose investors to the price of gold without having to take physical possession of the metal.
- Trade gold futures, which are agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of gold at a set price on a future date.
- Buy gold mining stocks. The value of these stocks is tied to the performance of the mining company and the price of gold.
The demand for gold for investment purposes has continuously increased in recent years, mainly after 2020.
2. Global financial reserves

For centuries, nations across the globe have added gold to their financial reserves as a valuable asset.
- Central banks today have amassed over 35,000 metric tons of gold in their holdings.
- Some countries with high gold reserves are the United States, Germany, Italy, France, China, Russia, and Switzerland.
Gold maintains its purchasing power through times of global uncertainty and market volatility. Central banks buy gold as a hedge against weakening fiat currencies to safeguard their financial systems.
3. Jewelry

Gold has been a favorite in making ornaments and jewelry for millennia. It boasts a lovely shine, a beautiful yellow color, and tarnish resistance. Gold can be cast into various shapes or hammered into sheets, making it perfect for crafting jewelry.
- Because pure gold is naturally soft, jewelry makers alloy gold with platinum, silver, copper, and other metals to craft strong and durable ornaments.
- Some jewelry pieces contain solid gold, whereas others feature gold plating over a base metal.
- Due to its rarity, gold is associated with wealth and status.
4. Electronics
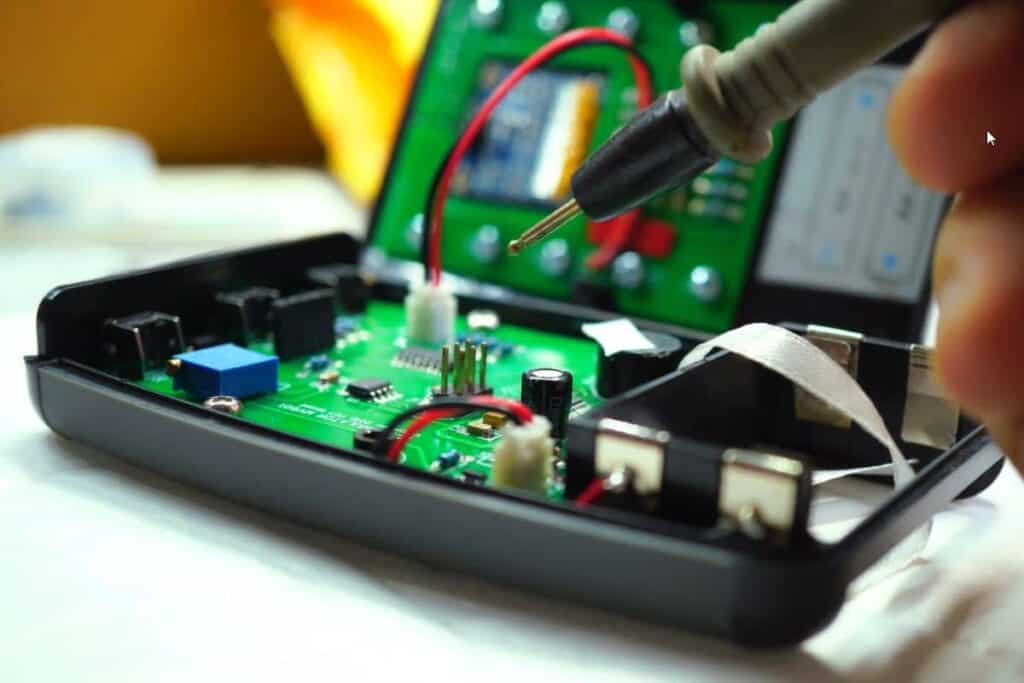

Gold is a vital part of numerous electrical and electronic components. It has superior corrosion resistance, outstanding electrical conductivity, and excellent wear resistance when alloyed with other metals, making it perfect for electronic industrial applications.
The most notable application of gold in electronics involves electroplated coatings on contacts and connectors. Other uses include gold bonding wires, solderable overlays for printed circuit boards, and hybrid circuits.
You can recover gold from electronics, devices and appliances, like smartphones, microwaves, televisions, and computers.
5. Medicinal Applications
For medical applications, one of the best qualities of gold is its superb biocompatibility. This means it does not cause adverse effects when in contact with skin and organs during medical operations.
Gold is an excellent plating material and component in numerous medical devices, surgical instruments, and electronic equipment, including:
- Scopes
- Wires for pacemakers
- Stents
- Acupuncture needles
- Implants and hearing aids
- Housings
- Battery casings
- Plastic metallization
- Electrodes for electrophysiology
- Diagnostics tests
- Wound dressings
Additionally, nanotechnology breakthroughs led to the use of gold nanoparticles in diagnosing cancer. These nanoparticles serve as an x-ray contrast agent to help doctors identify a tumor’s size and location. With the ability to serve as a drug delivery system, gold nanoparticles can be a potential cancer treatment.
Gold compounds have also been used to treat skin conditions such as pemphigus vulgaris and cutaneous lupus.
Gold injections were previously used as a treatment option for rheumatoid arthritis. However, they are no longer recommended in the U.S. today due to severe side effects.
6. Dentistry
Gold has been a reliable solution for tooth repair for thousands of years.
Besides its aesthetics, gold is known for its chemical inertness and durability. That means it will not rust or corrode despite exposure to saliva and enzymes in the mouth, making it perfect for use in dental work.
In modern dentistry, dentists use gold alloys and gold fillings to protect and restore teeth through these applications:
- Dental crowns made from gold are strong and can withstand the forces of biting and chewing.
- Inlays and onlays made from gold are used for teeth that are damaged but not enough to need a crown.
- Fixing small cavities
- Bridges made from gold are used for replacing missing teeth. They are anchored to the remaining teeth.
- Dental fillings are long-lasting, durable, and do not rust or tarnish.
- Orthodontic brackets and wires made from gold are biocompatible and do not cause allergic reactions, making them a good option for people with sensitive teeth.
Gold is a pricey but long-lasting dental solution. Gold fillings can last anywhere from 15 to 30 years, whereas dental crowns typically last up to 20 years.
7. Aerospace
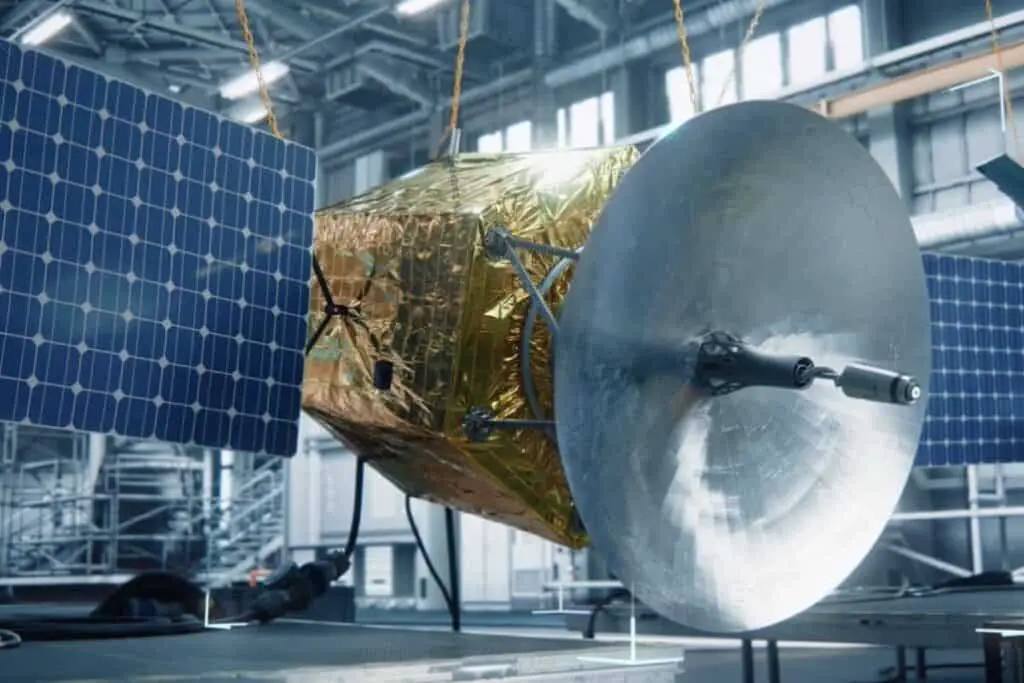

Gold is immensely valuable in the aerospace industry.
- Astronauts wear suits with thin layers of gold to protect against radiation and the sun’s scorching heat.
- Gold is also used in the helmets of astronauts and satellites.
In aeronautical circuitry, gold serves as a reliable conductor and connector.
- It adds durability to parts and components, ensuring they withstand long-term use in outer space without constant repair and maintenance.
- Many circuitry parts feature gold-coated polyester film to reflect infrared radiation and help stabilize aircraft temperatures.
Additionally, gold helps lubricate mechanical parts since organic lubricants are typically unstable. Thanks to its malleability, gold is easy to process into thin films for coating and protecting critical moving parts.
Gold is quite expensive. But in the billion-dollar aerospace industry, it is a small price to pay for the assurance of better safety when traveling thousands of miles outside Earth.
8. Window coatings and gold decoration in buildings

Gold reflects electromagnetic radiation, including solar radiation, radio waves, and visible light. Plus, it is highly malleable.
These metal qualities make gold an excellent solution for designing windows that minimize sun glare and heat in buildings.
Architects design heat-reflective windows to keep buildings cool in summer and warm in winter. The windowmaking process involves vacuum-depositing a thin gold layer between glass sheets. Or adding a coating of gold nanoparticles.
However, these gold-glazed windows have exorbitant prices.
- A famous building that uses these luxurious windows is the Sydney Opera House, which shields thousands of audience members from the sun.
- The Canadian Royal Bank Plaza Towers amazingly have gold in all 14,000 windows.
Some grand buildings also use gold adornments.
- The Criterion Restaurant in London boasts a lavish gold leaf ceiling.
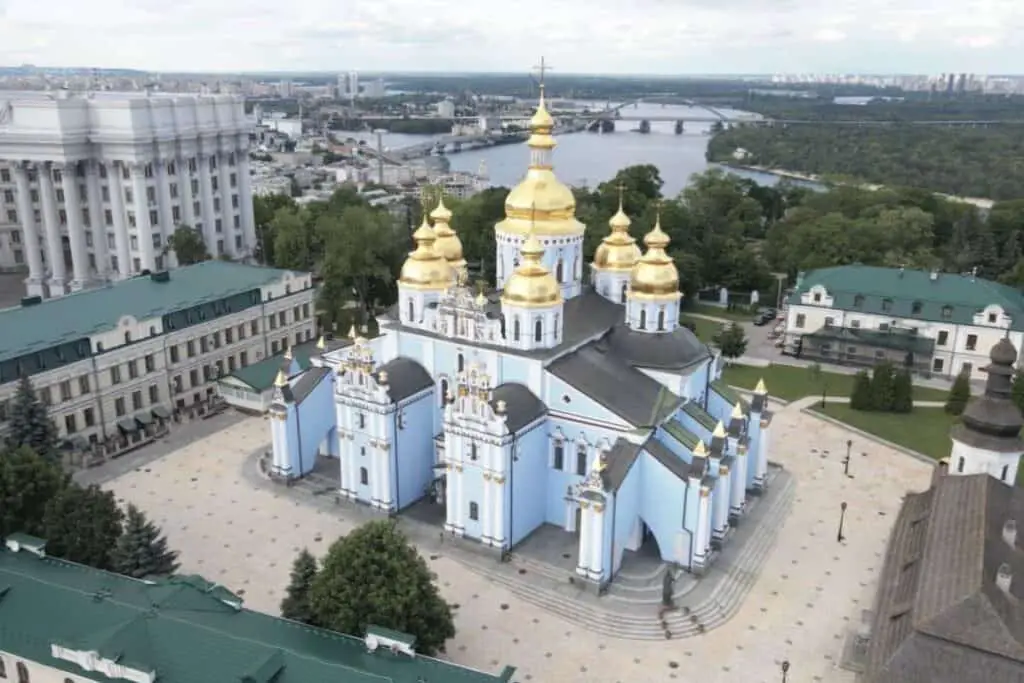
- St. Michael’s Cathedral in Ukraine showcases stunning golden domes.
9. Skincare and cosmetics
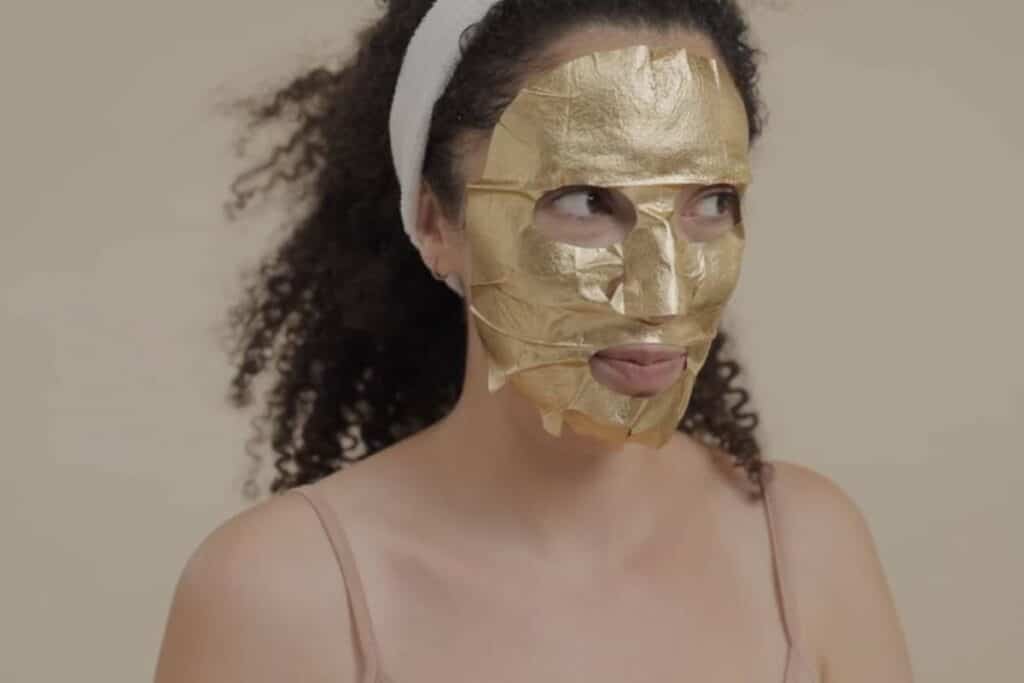

There has been much hype over gold facials and beauty products in recent years.
Many cosmetic companies today use gold nanoparticles to enhance cosmetic formulations in skin care products, including moisturizers, facial masks, lotions, eye creams, lip balms, and sunscreens. These products contain a mixture of skin-soothing ingredients and real gold.
- Businesses that provide these gold-infused products and cosmetic treatments claim that gold provides skin-boosting properties.
- They claim that gold helps improve collagen production, reduce inflammation, and fight the signs of aging.
However, there are currently no FDA-approved dermatological applications for gold.
10. Luxury food and drinks
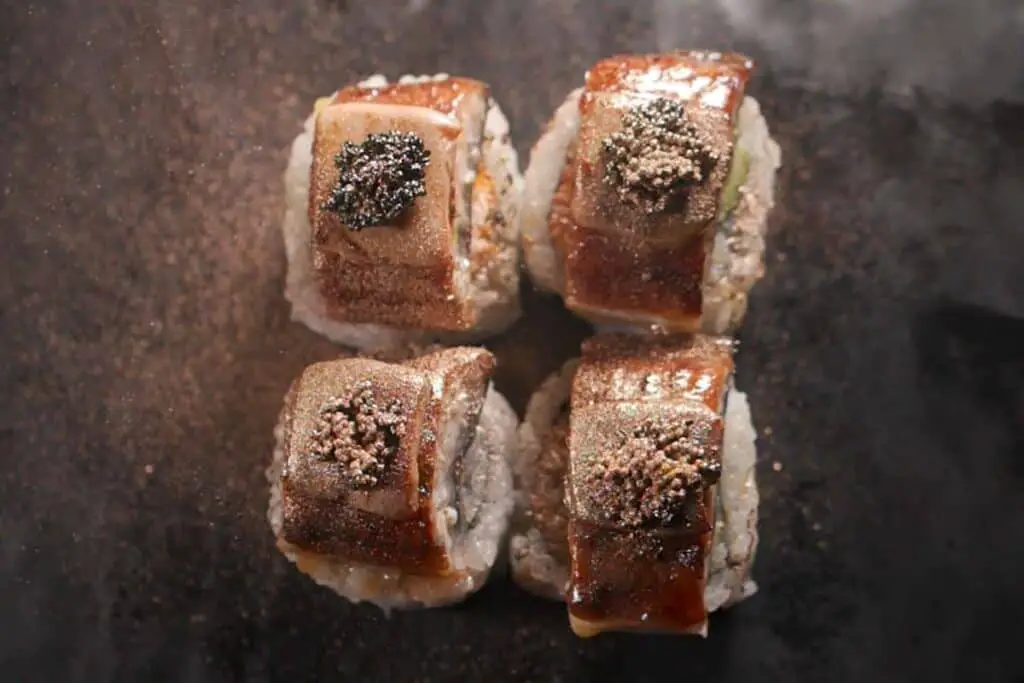

If you fancy a glittering dish, some high-end restaurants serve gold-decorated food, such as gold-topped burgers and ice cream cones sprinkled with gold shavings.
Recipes with food-grade gold do not offer any benefits or adverse effects. Gold is tasteless.
The use of edible gold is purely for decorative purposes.
- It is commonly used in gourmet restaurants and luxury hotels where they serve visually appealing, extravagant meals.
- Edible gold is non-toxic and biologically inert, making it acceptable for consumption.
The United States and European Union authorize the use of edible gold as a food additive.
FAQs about the modern uses of gold
Is gold continually recycled?
Gold is continually recycled, usually through dated jewelry pieces melted for reuse. Gold from end-of-life electronics also contributes to global recycled gold.
Is gold used in glassmaking?
Gold is used in glassmaking to craft luxurious glassware, including decorative mirrors, art frames, tableware, and chandeliers. This process involves fusing gold leaves between two glass layers.
What are other modern uses of gold?
Other modern uses of gold include the plating of medals and trophies in prestigious competitions, such as the Olympics. Additionally, some people use gold ink for printing high-quality, long-lasting photos.
Written by Jane Pardo

Jane Pardo is our senior gold & silver expert. Jane lends insight into precious metals investing, collecting, testing, and maintenance.
Trending posts under
As participant in an affiliate advertising program, we earn from qualifying purchases.